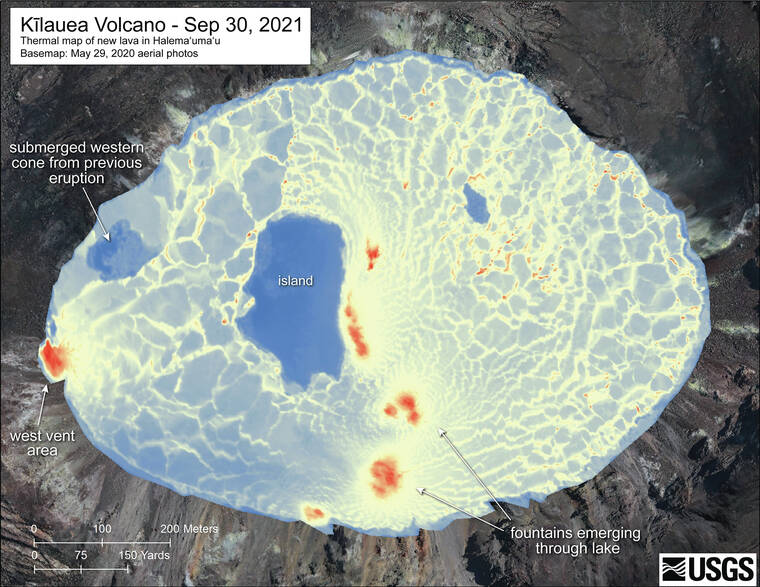
Kilauea volcano is erupting again. Wednesday afternoon, lava returned to Kilauea’s summit within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park after a 4-month hiatus. A new line of fissures sliced through the solidified crust of the 2020–21 lava lake in Halema‘uma‘u at 3:21 p.m. HST.
Like the prior eruption that began in December 2020, this new activity is confined entirely within Halema‘uma‘u. The new lava is continuing to fill the crater that collapsed in 2018 and is creating a new lava lake on top of the older one. Similar lava lakes frequently formed after collapse events in Halema‘uma‘u in the 1800s. This pattern of summit collapse and subsequent lava lake filling is one that Kilauea has exhibited in the past.
Both the December 2020 eruption and current eruption were immediately preceded by about an hour of elevated seismicity beneath Halema‘uma‘u. However, increased earthquake activity in the summit or upper East Rift Zone — as well as intrusions of magma beneath the summit region — provided clues of increased eruption potential prior to the eruptions.
Following the intrusion of magma into Kilauea’s south caldera and Southwest Rift Zone in late-August 2021, earthquake counts dropped to very low levels. Earthquake activity slightly increased on Sept. 24, breaking the one-month-long seismically quiet period.
A swarm of earthquakes began in the upper East Rift Zone beneath Pauahi Crater just before midnight on Sept. 28 and alerted HVO seismologists to an increase in activity. Overnight, smaller earthquakes were recorded closer to the summit followed by a smaller swarm near Puhimau Crater on Chain of Craters road within Hawai‘i Volcanoes National Park. After a relatively quite morning on Sept. 29, earthquake activity abruptly increased beneath Kilauea’s summit around 2 p.m. About 30 minutes later the intensity, frequencies, and shallowness of earthquakes coupled with rapid changes in ground deformation patterns, indicated magma was moving upward beneath Halema‘uma‘u.
These changes prompted the USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory to issue a Volcanic Activity Notice and Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation, elevating Kilauea’s Volcano Alert Level and Aviation Color Code to WATCH/ORANGE at 3:09 p.m. The change in status indicated that an eruption could be imminent and fissures opened in the floor of Halema‘uma‘u less than 20 minutes later. A second VAN/VONA was released, raising Kilauea’s Volcano Alert Level and Aviation Color Code to WARNING/RED to notify the public and emergency managers that a new Kilauea summit eruption had begun.
Summit tiltmeters began to record a higher rate of inflationary tilt during the 40 minutes preceding the start of the eruption; a total of 11 microradians at the nearest instrument. After the onset of the eruption, the tilt changed to a steady deflationary trend that is continuing.
Immediately before lava erupted, uplift of the older, solidified crust was seen in a few webcam image frames in the area where the fissures opened. The initial fissure cut across the middle of the Halema‘uma‘u crater floor and was followed about an hour later (around 4:40 p.m.) by a fissure with several vents on the western wall of Halema‘uma‘u. Multiple active vents continue to feed the growing lava lake that has risen approximately 20 m (65 ft) since the eruption started. The tallest lava fountain, near the southern end of the lava lake, has been measured at sustained heights of approximately 20–25 m (65–82 ft) throughout the night and into the morning of Sept. 30.
A preliminary calculation of the average eruption rate so far was approximately 120 cubic meters (4,238 cubic ft) per second resulting in a total erupted volume of roughly 10 million cubic meters (350 million cubic ft). These high eruption rates are accompanied by huge releases of volcanic gases — especially sulfur dioxide (SO2)—which is one of the primary hazards related to summit eruptions. Initial rates of SO2 emissions were measured at about 85,000 tonnes per day just after the start of the eruption.
The opening phases of eruptions can be unpredictable before the eruptive vents stabilize and HVO staff continue to monitor the ongoing eruption for any future changes. And while it’s not possible to predict exactly how long the current eruption may last, we expect that more summit and upper rift zone eruptions are likely in the coming years as Kilauea continues to re-pressurize and re-establish magma pathways after the 2018 eruption.
Volcano
activity updates
Kilauea volcano is erupting. Its USGS Volcano Alert level is at WARNING (https://www.usgs.gov/natural-hazards/volcano-hazards/about-alert-levels). Kilauea updates are issued daily.
Kilauea volcano is erupting. Lava continues to erupt from multiple vents along the floor and western wall of Halema‘uma‘u crater. As of this afternoon all lava activity is confined within Halema‘uma‘u crater. Sulfur dioxide emission rates remain high. Seismicity is elevated but stable, with few earthquakes and ongoing volcanic tremor. Summit tiltmeters continued to record slowing deflationary tilt. For more information on the current eruption of Kilauea, see Recent Eruption (usgs.gov).
Mauna Loa is not erupting and remains at Volcano Alert Level ADVISORY. This alert level does not mean that an eruption is imminent or that progression to an eruption from the current level of unrest is certain. Mauna Loa updates are issued weekly.
This past week, about 69 small-magnitude earthquakes were recorded below the summit and upper elevation flanks of Mauna Loa — the majority of these occurred at shallow depths less than 8 kilometers (5 miles). Global Positioning System measurements show no major deformation over the past week. Gas concentrations and fumarole temperatures at both the summit and at Sulphur Cone on the Southwest Rift Zone remain stable. Webcams show no changes to the landscape. For more information on current monitoring of Mauna Loa, see: https://www.usgs.gov/volcanoes/mauna-loa/monitoring.
There were 6 events with 3 or more felt reports in the Hawaiian Islands during the past week: a M2.5 earthquake 4 km (2 mi) WSW of Volcano at 0 km (0 mi) depth on Sept. 30 at 2:03 a.m. HST, a M2.8 earthquake 4 km (2 mi) WSW of Volcano at 0 km (0 mi) depth on Sept. 29 at 7:33 p.m. HST, a M2.8 earthquake 19 km (11 mi) NW of Kalaoa at 0 km (0 mi) depth on Sept. 29 at 5:10 p.m. HST, a M2.6 earthquake 5 km (3 mi) WSW of Volcano at 0 km (0 mi) depth on Sept. 29 at 3:04 p.m. HST, a M2.9 earthquake 5 km (3 mi) S of Pahala at 33 km (20 mi) depth on Sept. 28 at 9:54 a.m. HST, and a M3.8 earthquake 1 km (0 mi) SSW of Pahala at 33 km (21 mi) depth on Sept. 27 at 3:42 a.m. HST.
HVO continues to closely monitor Kilauea’s ongoing eruption and Mauna Loa for any signs of increased activity.
Email questions to askHVO@usgs.gov.
Volcano Watch is a weekly article and activity update written by U.S. Geological Survey Hawaiian Volcano Observatory scientists and affiliates.