CDC extends travel mask mandate to May 3 as COVID-19 cases rise
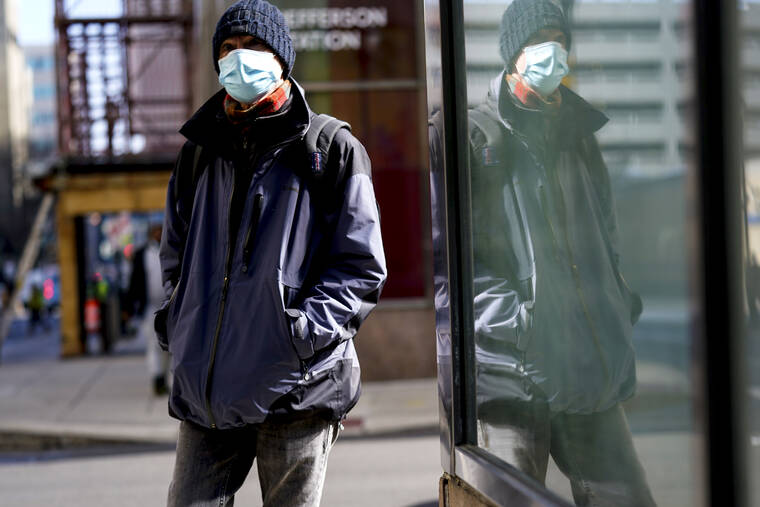

FILE - A person wearing a face masks to protect against the spread of the coronavirus walks in Philadelphia, Feb. 16, 2022. The Biden administration will extend for two weeks the nationwide mask requirement for public transit as it monitors an uptick in COVID-19 cases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention was set to extend the order, which was to expire on April 18, by two weeks to monitor for any observable increase in severe virus outcomes as cases rise in parts of the country. (AP Photo/Matt Rourke, FILE
WASHINGTON — The Biden administration announced Wednesday that it is extending the nationwide mask requirement for airplanes and public transit for 15 days as it monitors an uptick in COVID-19 cases.
WASHINGTON — The Biden administration announced Wednesday that it is extending the nationwide mask requirement for airplanes and public transit for 15 days as it monitors an uptick in COVID-19 cases.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said it was extending the order, which was set to expire on April 18, until May 3 to allow more time to study the BA.2 omicron subvariant that is now responsible for the vast majority of cases in the U.S.
ADVERTISING
“In order to assess the potential impact the rise of cases has on severe disease, including hospitalizations and deaths, and health care system capacity, the CDC order will remain in place at this time,” the agency said in a statement.
When the Transportation Security Administration, which enforces the rule for planes, buses, trains and transit hubs, extended the requirement last month, it said the CDC had been hoping to roll out a more flexible masking strategy that would have replaced the nationwide requirement.
The mask mandate is the most visible vestige of government restrictions to control the pandemic, and possibly the most controversial. A surge of abusive and sometimes violent incidents on airplanes has been attributed mostly to disputes over mask-wearing.
Separately, the Biden administration also extended for 90 days a public health emergency that has been in effect since early 2020. That allows temporary continuation of a range of public health measures that do have broad support, from more generous Medicaid coverage to flexibility around telehealth.
The mask requirement for travelers was the target of months of lobbying from the airlines, who sought to kill it. The carriers argued that effective air filters on modern planes make transmission of the virus during a flight highly unlikely. Republicans in Congress also fought to kill the mandate.
Critics have seized on the fact that states have rolled back rules requiring masks in restaurants, stores and other indoor settings, and yet COVID-19 cases have fallen sharply since the omicron variant peaked in mid-January.
“It is very difficult to understand why masks are still required on airplanes, but not needed in crowded bars and restaurants; in packed sports arenas; in schools full of children; or at large indoor political gatherings,” Nicholas Calio, the CEO of industry trade group Airlines for America, said Wednesday in a letter to the heads of the CDC and the Health and Human Services Department. “Simply put, an extension of the mask mandate does not make sense.”
There has been a slight increase in cases in recent weeks, with daily confirmed cases nationwide rising from about 25,000 per day to more than 30,000. More than 85% of those cases are the highly contagious BA.2 strain. Those figures could be an undercount since many people now test positive on at-home tests that are not reported to public health agencies.
Severe illnesses and deaths tend to lag infections by several weeks. The CDC is awaiting indications of whether the increase in cases correlates to a rise in adverse outcomes before announcing a less restrictive mask policy for travel.
A poll in mid-March by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that Americans are evenly divided over keeping the mask rule for transportation.
The poll found that 51% wanted the mandate to expire and 48% said it should remain in place – in effect, a tie, given the poll’s margin of error. Democrats overwhelmingly supported the rule, and Republicans were even more united in opposing it. Vaccinated people and those with chronic health conditions favored keeping the rule, but by smaller margins.
Airlines imposed their own mask mandates in 2020, when the Trump administration declined to take action. Unions representing flight attendants, which once backed mask rules, now decline to take a position because their members are divided over the issue.
It is unclear whether eliminating the rule would make people more or less likely to travel on planes or subways.
Ed Bastian, the CEO of Delta Air Lines, said that some people might start flying if they don’t have to wear a mask, and others might stop flying if other passengers are unmasked. He called both groups “fringe,” and he predicted that many people will continue to wear masks even if the rule is dropped.
As for the broader public health emergency just extended by the Department of Health and Human Services, the administration has promised to give states 60 days’ notice before ending it.
Winding down the emergency declaration could force an estimated 15 million Medicaid recipients to find new sources of coverage, require congressional action to preserve broad telehealth access for Medicare enrollees, and scramble special COVID-19 rules and payment policies for hospitals, doctors and insurers. There are also questions about how emergency use approvals for COVID-19 treatments will be handled.