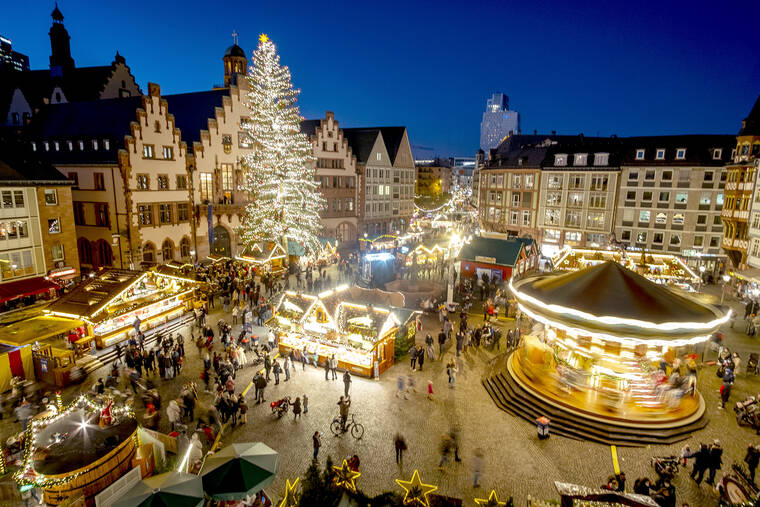
FRANKFURT, Germany — The holiday tree is towering over the main square in this central German city, the chestnuts and sugared almonds are roasted, and kids are clambering aboard the merry-go-round just like they did before the pandemic. But a surge in coronavirus infections has left an uneasy feeling hanging over Frankfurt’s Christmas market.
To savor a mug of mulled wine — an uncomplicated rite of winter in pre-pandemic times — masked customers must pass through a one-way entrance to a fenced-off wine hut, stopping at the hand sanitizer station. Elsewhere, security officers check vaccination certificates before letting customers head for the steaming sausages and kebabs.
Despite the pandemic inconveniences, stall owners selling ornaments, roasted chestnuts and other holiday-themed items in Frankfurt and other European cities are relieved to be open at all for their first Christmas market in two years, especially with new restrictions taking effect in Germany, Austria and other countries as COVID-19 infections hit record highs. Merchants who have opened are hoping for at least a fraction of the pre-pandemic holiday sales that can make or break their businesses.
Others aren’t so lucky. Many of the famous holiday events have been canceled in Germany and Austria. With the market closures goes the money that tourists would spend in restaurants, hotels and other businesses.
Jens Knauer, who crafts intricate, lighted Christmas-themed silhouettes that people can hang in windows, said his hope was simply that the Frankfurt market “stays open as long as possible.”
While Christmas is 40% of annual revenue for many retailers and restaurateurs, “with me, it’s 100%,” Knauer said. “If I can stay open for three weeks, I can make it through the year.”
Purveyors are on edge after other Christmas markets were abruptly shut down in Germany’s Bavaria region, which includes Nuremberg, home of one of the biggest and best-known markets. Stunned exhibitors in Dresden had to pack up their goods when authorities in the eastern Saxony region suddenly imposed new restrictions amid soaring infections. Austria’s markets closed as a 10-day lockdown began Monday, with many stall owners hoping they can reopen if it’s not extended. The Czech government on Thursday closed Christmas markets as part of measures to counter a record surge in cases.
Markets usually attract elbow-to-elbow crowds to row upon row of ornament and food sellers, foot traffic that spills over into revenue for surrounding hotels and restaurants. This year, the crowds at Frankfurt’s market were vastly thinned out, with the stalls spread out over a larger area.
Heiner Roie, who runs a mulled wine hut in the shape of a wine barrel, said he’s assuming he will see half the business he had in 2019. A shutdown would cause “immense financial damage — it could lead to complete ruin since we haven’t made any income in two years, and at some point, the financial reserves are used up.”
But if people have a little discipline and observe the health measures, “I think we’ll manage it,” he said.
Next door, Bettina Roie’s guests are greeted with a sign asking them to show their vaccination certificates at her stand serving Swiss raclette, a popular melted cheese dish.
The market “has a good concept because what we need is space, room, to keep some distance from each other,” she said. “In contrast to a bricks-and-mortar restaurant, they have their building and their walls, but we can adjust ourselves to the circumstances.”
The extended Roie family is a fifth-generation exhibitor business that also operates the merry-go-round on Frankfurt’s central Roemerberg square, where the market opened Monday.
Roie said it was important to reopen “so that we can bring the people even during the pandemic a little joy — that’s what we do, we bring back joy.”
The latest spike in COVID-19 cases has unsettled prospects for Europe’s economic recovery, leading some economists to hedge their expectations for growth in the final months of the year.
Holger Schmieding, chief economist at Berenberg Bank in London, has cut his forecast for the last three months of the year in the 19 countries that use the euro from 0.7% to 0.5%. But he noted that the wave of infections is having less impact across the broad economy because vaccinations have reduced serious illnesses and many companies have learned to adjust.
That is cold comfort to Germany’s DEHOGA restaurant and hotel association, which warned of a “hail of cancellations” and said members were reporting every second Christmas party or other special event was being called off.